在qiankun的源码中,使用了 import-html-entry 库来加载html,这里实现下一个简版的import-html-entry来介绍微前端的第一步怎么去加载子应用资源。
import-html-entry
首先简单介绍下import-html-entry使用方法
import importHTML from 'import-html-entry';
interface IOpts {
fetch?: Function;
getPublicPath?: (url: string) => string;
getDomain?: (url: string) => string;
getTemplate?: (html: string) => html;
}
interface ILifeCycle {
bootstrap?: (props: any) => Promise<void>;
mount?: (props: any) => Promise<void>;
unmount?: (props: any) => Promise<void>;
}
interface IImportReturn {
template: string;
assetPublicPath: string;
getExternalScripts: () => Promise<string[]>;
getExternalStyleSheets: () => Promise<string[]>;
execScripts: (proxy: any) => Promise<ILifeCycle>;
}
interface IImportHTML {
(url: string, opts?: Function | IOpts): Promise<IImportReturn>;
}
async function () {
const { template, execScripts, assetPublicPath } = await importHTML('http://localhost:8082');
} import-html-entry默认导出importHtml方法,接收2个参数
import-html-entry默认导出importHtml方法,接收2个参数
- url html地址
- opts 可选,如果传入函数则会作为自定义fetch
如果所示,返回一个对象
- template 已做处理的html模板字符串
- assetPublicPath 资源的根路径地址
- getExternalScripts 获取外部引用样式文件的方法
- getExternalStyleSheets 获取外部引用脚本文件的方法
- execScripts 执行子应用的脚本文件的方法,可以传入proxy指定作用域
在qiankun的源码中,主要用到了 template 作为子应用容器的内容,execScripts(proxy) 调用子应用js,并获取子应用的生命周期
importHTML
importHTML是import-html-entry默认导出的方法,这里简化成接收一个html url参数。其中import-html-entry是可以传入自定义fetch方法的,这里直接使用封装fetch的request方法。
import { request, defaultGetPublicPath } from '../utils';
interface IEmbedHTMLCache {
[url: string]: Promise<IImportReturn>;
}
const embedHTMLCache: IEmbedHTMLCache = {};
export default function importHTML(url: string): Promise<IImportReturn> {
return embedHTMLCache[url] ||
(embedHTMLCache[url] = request(url).then((html: string) => {
console.log(html);
}));
}importHTML函数内部首先会做一层缓存,然后fetch请求html字符串
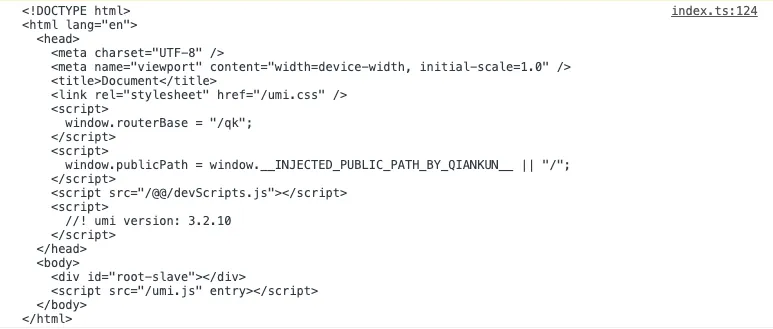
当然这种html的字符串不能直接使用,import-html-entry会使用 processTpl 方法对字符串进行处理,返回处理好的模板字符串、script、style等。
processTpl
processTpl主要使用正则去收集style script,处理对应的字符串。主要流程:
- 去除html注释
- 查找link标签
- 查找style标签
- 查找所有的script标签
最后返回出处理后的字符串、scripts 数组、styles 数组 以及 entry
export default function processTpl(tpl: string, baseURI: string) {
const styles: string[] = [];
let scripts: string[] = [];
let entry = null;
const template = tpl
// 去除html注释 <!-- xxx -->
.replace(HTML_COMMENT_REGEX, '')
// 查找link标签
.replace(LINK_TAG_REGEX, (match) => {})
// 查找style标签
.replace(STYLE_TAG_REGEX, (match) => {})
// 查找所有的script标签
.replace(ALL_SCRIPT_REGEX, (match) => {})
scripts = scripts.filter(function (script) {
// 过滤空script
return !!script;
});
return {
template,
scripts,
styles,
entry: entry || scripts[scripts.length - 1], // 把最后一个script作为入口
};
}去除html注释
const HTML_COMMENT_REGEX = /<!--([\s\S]*?)-->/g;
const template = tpl
// 去除html注释 <!-- xxx -->
.replace(HTML_COMMENT_REGEX, '')去除html注释比较简单,使用replace将 注释中任意内容替换为空字符串
查找link标签
const LINK_TAG_REGEX = /<(link)\s+.*?>/gi;
const STYLE_TYPE_REGEX = /\s+rel=('|")?stylesheet\1.*/;
const template = tpl
// 查找link标签
.replace(LINK_TAG_REGEX, (match) => {
// 查找是否是 link style 样式标签
const styleType = !!match.match(STYLE_TYPE_REGEX);
if (styleType) {
// 查找 link 标签中的 href
const styleHref = match.match(STYLE_HREF_REGEX);
if (styleHref) {
const href = styleHref && styleHref[2]; // /umi.css
let newHref = href;
// 获取完整路径
if (href && !hasProtocol(href)) {
newHref = getEntirePath(href, baseURI); // http://localhost:8082/umi.css
}
styles.push(newHref);
return `<!-- ${newHref} -->`; // 注释link标签
}
}
return match;
})第二步查询link标签,判断是否是style link(ref="stylesheet")提取href,组合成完整的href路径存入styles数组中,最后用html注释替换掉link标签。
其中用到了2个方法 hasProtocol 是判断是否有protocol,判断url开发是否是// http:// 或者 https://
/**
* 判断是否有Protocol
* @example
* //www.test.com
* http://www.test.com
* https://www.test.com
*/
function hasProtocol(url: string) {
return url.startsWith('//') || url.startsWith('http://') || url.startsWith('https://');
}getEntirePath则可以根据 path baseURI组成一个完整url
/**
* 获取完整路径
* @example
* new URL('/a', 'http://www.test.com').toString();
* "http://www.test.com/a"
*/
function getEntirePath(path: string, baseURI: string) {
return new URL(path, baseURI).toString();
}查找style标签 **
const template = tpl
// 查找style标签
.replace(STYLE_TAG_REGEX, (match) => {
// ... style ignore判断
return match;
})在import-html-entry中会对
<style ignore>xxx</style>带有ignore的style标签进行过滤,这里就不做处理了
查找所有的script标签 ** script标签一般分为2种,一个是
<script src="./umi.js"></script>通过 src 属性指向外部脚本文件,另一个是
<script>console.log('1')</script>包含脚本语句。
外链
const ALL_SCRIPT_REGEX = /<script\b[^<]*(?:(?!<\/script>)<[^<]*)*<\/script>/gi;
const SCRIPT_TAG_REGEX = /<(script)\s+((?!type=('|')text\/ng-template\3).)*?>.*?<\/\1>/is;
const SCRIPT_SRC_REGEX = /.*\ssrc=('|")?([^>'"\s]+)/;
const template = tpl
.replace(ALL_SCRIPT_REGEX, (match) => {
// ... script ignore 判断
// ... script module 判断
// ... script type 判断
// 判断是否是 外链script <script src="/umi.js"></script>
if (SCRIPT_TAG_REGEX.test(match) && match.match(SCRIPT_SRC_REGEX)) {
// ... script enter 判断 <script src="/umi.js" enter></script>
const matchedScriptSrcMatch = match.match(SCRIPT_SRC_REGEX);
let matchedScriptSrc = matchedScriptSrcMatch && matchedScriptSrcMatch[2]; // /umi.js
if (matchedScriptSrc && !hasProtocol(matchedScriptSrc)) {
// 获取完整script路径
matchedScriptSrc = getEntirePath(matchedScriptSrc, baseURI);
}
if (matchedScriptSrc) {
scripts.push(matchedScriptSrc);
return `<!-- ${matchedScriptSrc} -->`;
}
}
return match;
})判断是外链的script标签,获取src,组成完成的src路径存入scripts数组中,最后用html注释替换掉script标签。处理方法跟style link类似。
内嵌
const ALL_SCRIPT_REGEX = /<script\b[^<]*(?:(?!<\/script>)<[^<]*)*<\/script>/gi;
const SCRIPT_TAG_REGEX = /<(script)\s+((?!type=('|')text\/ng-template\3).)*?>.*?<\/\1>/is;
const SCRIPT_SRC_REGEX = /.*\ssrc=('|")?([^>'"\s]+)/;
function getInlineCode(match: string) {
const start = match.indexOf('>') + 1;
const end = match.lastIndexOf('<');
return match.substring(start, end);
}
const template = tpl
.replace(ALL_SCRIPT_REGEX, (match) => {
// ... script ignore 判断
// ... script module 判断
// ... script type 判断
// 判断是否是 外链script <script src="/umi.js"></script>
if (SCRIPT_TAG_REGEX.test(match) && match.match(SCRIPT_SRC_REGEX)) {
// ...
} else { // 判断是否是 内嵌script
// ... script ignore 判断
// ... script module 判断
// 获取内嵌script code
const code = getInlineCode(match);
/**
* 判断是否只是注释代码
* @example
* <script>
* //! umi version: 3.2.10
* </script>
*/
const isPureCommentBlock = code.split(/[\r\n]+/).every(line => !line.trim() || line.trim().startsWith('//'));
if (!isPureCommentBlock) {
scripts.push(match);
}
return `<!-- script -->`
}
return match;
})获取到内嵌script的内容会进行简单处理,判断每一行是否都是 // 单行注释开头,判断是否是单纯的注释 比如
<script>
// 注释
// 注释
// 注释
</script>如果不是纯注释则添加到scripts数组中,script标签替换成注释。 似乎没有判断块级注释?
综上,scripts数组中可能会出现2种内容,script src 和 script code。
getEmbedHTML
在通过processTpl方法获取处理后的html字符串后,需要使用getEmbedHTML进行进一步处理,主要请求css资源,挂载到html中。 在qiankun中,子应用的样式是动态加载的,所以需要获取css资源,添加style标签添加到html中,当子应用卸载时,同时移除style标签就能移除子应用样式。
export default function importHTML(url: string): Promise<IImportReturn> {
return embedHTMLCache[url] ||
(embedHTMLCache[url] = request(url).then((html: string) => {
const { template, scripts, entry, styles } = processTpl(html, defaultGetPublicPath(url));
const assetPublicPath = defaultGetPublicPath(url);
return getEmbedHTML(template, styles).then(embedHTML => ({
template: embedHTML,
assetPublicPath,
getExternalScripts: () => getExternalScripts(scripts),
getExternalStyleSheets: () => getExternalStyleSheets(styles),
execScripts: (proxy: any) => {
if (!scripts.length) {
return Promise.resolve();
}
return execScripts(entry, scripts, proxy);
},
}));
}));
}// 获取完整的html
function getEmbedHTML(template: string, styles: string[]) {
let embedHTML = template;
// 请求css,挂载到html中
return getExternalStyleSheets(styles)
.then(styleSheets => {
embedHTML = styles.reduce((html, styleSrc, i) => {
html = html.replace(`<!-- ${styleSrc} -->`, `<style>/* ${styleSrc} */${styleSheets[i]}</style>`);
return html;
}, embedHTML);
return embedHTML;
});
}getEmbedHTML内部主要使用getExternalStyleSheets方法去获取style样式表,找到到原先在processTpl中标记的 link标签注释 进行替换。
getExternalStyleSheets **
const styleCache: IStyleCache = {};
const isInlineCode = (code: string) => code.startsWith('<');
function getInlineCode(match: string) {
const start = match.indexOf('>') + 1;
const end = match.lastIndexOf('<');
return match.substring(start, end);
}
export function getExternalStyleSheets(styles: string[]) {
return Promise.all(styles.map(styleLink => {
if (isInlineCode(styleLink)) {
// 如果是内联style(感觉不存在这个情况)
return getInlineCode(styleLink);
} else {
// 请求 http://localhost:8082/umi.css
return styleCache[styleLink] ||
(styleCache[styleLink] = request(styleLink));
}
},
));
}getExternalStyleSheets 接收styles数组,通过 Promise.all 并发请求 css 资源,不过在processTpl处理后的styles 理应只储存 link href 没有内联的样式,所以感觉内联样式判断好像是多余的?
execScripts
execScripts是执行脚本的方法,可以传入指定作用域,一般有2种用法,第一种是 importHTML 方法最后返回的 execScripts,内部会调用子应用所有的script,并resolve出子应用导出的 bootstrap mount unmount 。另外也可以单独使用,比如qiankun劫持appendChild监听到动态加载了新的script,便可以调用execScripts进行劫持处理。
export function execScripts(entry: string, scripts: string[], proxy = window): Promise<ILifeCycle> {
return getExternalScripts(scripts)
.then(scriptsText => {
const geval = eval;
function exec(scriptSrc: string, inlineScript: string, resolve: Function) {}
function schedule(i: number, resolvePromise: Function) {}
return new Promise(resolve => schedule(0, resolve));
});
}在execScripts内部中,首页会 getExternalScripts 获取script脚本,原理同 getExternalStyleSheets
export function getExternalScripts(scripts: string[]) {
// 请求script方法
const fetchScript = (scriptUrl: string) => scriptCache[scriptUrl] ||
(scriptCache[scriptUrl] = request(scriptUrl));
return Promise.all(scripts.map(script => {
if (typeof script === 'string') {
if (isInlineCode(script)) {
// 内联script
return getInlineCode(script);
} else {
// 外链
return fetchScript(script);
}
} else {
// ... async script 处理
}
}
));
}在获取到script脚本后,递归schedule方法,执行script。
function schedule(i: number, resolvePromise: Function) {
if (i < scripts.length) {
const scriptSrc = scripts[i];
const inlineScript = (scriptsText[i] as string);
exec(scriptSrc, inlineScript, resolvePromise);
// resolve the promise while the last script executed and entry not provided
if (!entry && i === scripts.length - 1) {
resolvePromise();
} else {
schedule(i + 1, resolvePromise);
}
}
}
return new Promise(resolve => schedule(0, resolve));exec
const geval = eval;
function exec(scriptSrc: string, inlineScript: string, resolve: Function) {
if (scriptSrc === entry) {
noteGlobalProps(window);
// bind window.proxy to change `this` reference in script
// 运行可执行js
geval(getExecutableScript(scriptSrc, inlineScript, proxy));
// @ts-ignore
const exports = proxy[getGlobalProp(window)] || {};
resolve(exports);
} else {
if (typeof inlineScript === 'string') {
// bind window.proxy to change `this` reference in script
geval(getExecutableScript(scriptSrc, inlineScript, proxy));
} else {
// ... async script 处理
}
}
}在exec方法中,会使用 getExecutableScript 来将script转化成可执行的script(bind this、指定作用域),并用eval执行。
function getExecutableScript(scriptSrc: string, scriptText: string, proxy: any) {
const sourceUrl = isInlineCode(scriptSrc) ? '' : `//# sourceURL=${scriptSrc}\n`;
window.proxy = proxy;
return `;(function(window, self){;${scriptText}\n${sourceUrl}}).bind(window.proxy)(window.proxy, window.proxy);`;
}qiankun子应用中需要修改下webpack配置,设置library,将libraryTarget设置成umd,并且入口文件导出生命周期钩子。
const packageName = require('./package.json').name;
module.exports = {
output: {
library: "qk-c-umi",
libraryTarget: 'umd',
jsonpFunction: `webpackJsonp_${packageName}`,
},
};umd 模式会在打包出来的js中加入兼容的代码,执行后会在window上添加 qk-c-umi 属性
(function webpackUniversalModuleDefinition(root, factory) {
if(typeof exports === 'object' && typeof module === 'object')
module.exports = factory();
else if(typeof define === 'function' && define.amd)
define([], factory);
else if(typeof exports === 'object')
exports["qk-c-umi"] = factory();
else
root["qk-c-umi"] = factory();
})(window, function() {
return {
bootstrap,
mount,
unmount,
update,
}
});所以在exec中,要执行入口文件js时,需要找到window上挂载的 qk-c-umi 属性
if (scriptSrc === entry) {
noteGlobalProps(window);
// bind window.proxy to change `this` reference in script
// 运行可执行js
geval(getExecutableScript(scriptSrc, inlineScript, proxy));
// @ts-ignore
const exports = proxy[getGlobalProp(window)] || {};
resolve(exports);
}首先通过 noteGlobalProps 记录 window上 第1、2个和最后一个prop
export function noteGlobalProps(global: any) {
// alternatively Object.keys(global).pop()
// but this may be faster (pending benchmarks)
firstGlobalProp = secondGlobalProp = undefined;
for (let p in global) {
if (shouldSkipProperty(global, p))
continue;
if (!firstGlobalProp)
firstGlobalProp = p;
else if (!secondGlobalProp)
secondGlobalProp = p;
lastGlobalProp = p;
}
return lastGlobalProp;
}执行完js后通过 getGlobalProp 去找window上新增的属性
function shouldSkipProperty(global: any, p: string) {
if (
!global.hasOwnProperty(p) || // 跳过原型上的属性
!isNaN(p) && p < global.length
) {
return true;
}
if (isIE11) {
// https://github.com/kuitos/import-html-entry/pull/32,最小化 try 范围
try {
return global[p] && global[p].parent === window;
} catch (err) {
return true
}
} else {
return false
}
}
export function getGlobalProp(global: any) {
let cnt = 0;
let lastProp;
let hasIframe = false;
for (let p in global) {
if (shouldSkipProperty(global, p)) {
continue;
}
// 遍历 iframe,检查 window 上的属性值是否是 iframe,是则跳过后面的 first 和 second 判断
for (let i = 0; i < window.frames.length && !hasIframe; i++) {
const frame = window.frames[i];
if (frame === global[p]) {
hasIframe = true;
break;
}
}
if (!hasIframe && (cnt === 0 && p !== firstGlobalProp || cnt === 1 && p !== secondGlobalProp)) {
return p;
}
cnt++;
lastProp = p;
}
if (lastProp !== lastGlobalProp) {
return lastProp;
}
}上述代码中可以看出是遍历对象,找到最后一个属性名。 对象添加属性是按需添加的,但是数字/数字字符串的属性名会打乱顺序,所以这里进行了 first和second prop判断?
const obj = {};
obj.b = 'b';
obj.c = 'c';
obj.a = 'a';
Object.keys(obj); // ["b", "c", "a"]
obj['2'] = '2';
obj['1'] = '1';
Object.keys(obj); // ["1", "2", "b", "c", "a"]不过window对象倒是添加不了数字/数字字符串的属性名。总体看这段代码还是有写疑惑的,比如为什么需要判断是否有iframe,极端情况下新增的属性也不一定能找到
importEntry
qiankun中就使用了importEntry,与importHTML相比多做了一层兼容,可以接收 scripts styles 参数。这里就不做展开了。
interface IEntry {
scripts?: string[];
styles?: string[];
html?: string;
}
export function importEntry(entry: IEntry | string): Promise<IImportReturn> {
// html entry
if (typeof entry === 'string') {
return importHTML(entry);
}
// config entry
const { scripts = [], styles = [], html = '' } = entry;
// 生成style注释占位
const setStylePlaceholder2HTML = (tpl: string) => styles.reduceRight((html, styleSrc) => `<!--${styleSrc} -->${html}`, tpl);
// 生成script注释占位
const setScriptPlaceholder2HTML = (tpl: string) => scripts.reduce((html, scriptSrc) => `${html}<!-- ${scriptSrc} -->`, tpl);
return getEmbedHTML(setScriptPlaceholder2HTML(setStylePlaceholder2HTML(html)), styles)
.then(embedHTML => ({
template: embedHTML,
assetPublicPath: defaultGetPublicPath('/'),
getExternalScripts: () => getExternalScripts(scripts),
getExternalStyleSheets: () => getExternalStyleSheets(styles),
execScripts: (proxy: any) => {
if (!scripts.length) {
return Promise.resolve();
}
return execScripts(scripts[scripts.length - 1], scripts, proxy);
},
}));
}